YouTube supports both RTMP and HLS for live streaming. This article outlines which protocol is most suitable for different types of content, taking into account key factors such as latency, stability, and internet connection.
While various protocols exist for transmitting live streams to the platforms, YouTube specifically supports RTMP(Real-Time Messaging Protocol) and HLS(HTTP Live Streaming).
RTMP has been used for a long time and is considered the standard in the industry. In the case of HLS, it is becoming widely used not only for distribution to the end-user but also for the content ingest stage.
A different protocol means a different transmission method, and this difference has a significant impact on live streaming. By outlining the differences and characteristics of the two protocols in this article, the writer hopes to help readers choose the suitable protocol.
The Difference Between RTMP and HLS – Continuous
Although both the RTMP and HLS protocols are used to transmit and play video streams continuously, there is a significant difference in their methods as shown in the image below.
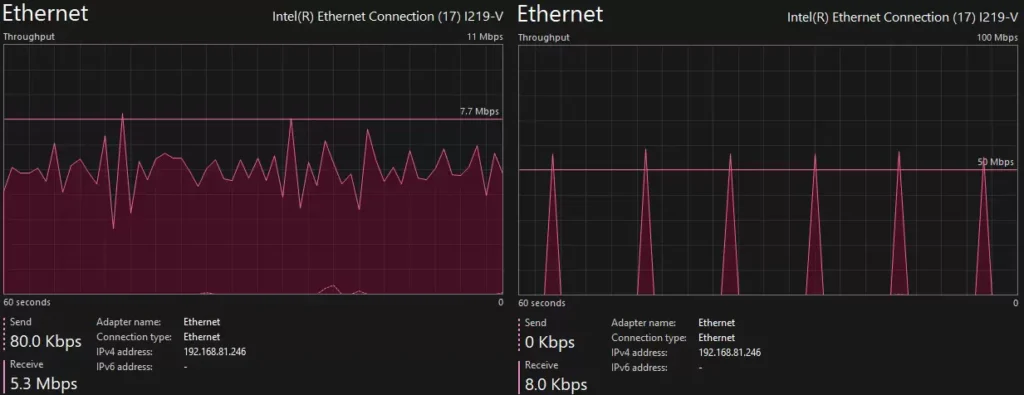
The graph above shows the network traffic of RTMP and HLS stream, using same MPEG2-TS UDP source stream on Wowza Streaming Engine. The graph on the left represents RTMP, and the graph on the right represents HLS.
A single glance reveals that the shapes of the graphs are very different. In the RTMP graph on the left, approximately 5 Mbps of network traffic is generated continuously. In contrast, the HLS graph on the right shows traffic repeatedly bursting to about 50 Mbps and then pausing, at 10-second intervals.
RTMP continuously transmits data received from an encoder in real time. This concept is similar to traditional broadcasting, where a radio station sends out a live signal over the airwaves, and a listener hears it at the same time on their radio.
HLS works by repeatedly transmitting video files created by collecting data from an encoder over a certain period. On the player side, if the next video file is added to the playlist before the current one finishes playing, the player can continue playing without stopping. The underlying principle is that by repeating this process, continuous, uninterrupted playback can be achieved.
To summarize, the differences in transmission methods between RTMP and HLS can be defined as follows:
- RTMP
- transmits video data continuously without interruption.
- It is similar to a real-time phone call or a radio broadcast.
- HLS
- It segments video data at regular intervals to create and upload video files.
- It plays video segment files sequentially, a concept similar to a relay race.
Latency vs Stability – Characteristics from Difference
As seen above, the key difference between RTMP and HLS is whether the stream is delivered continuously or in discrete segments. And, This difference leads to unique characteristics in stream playback.
HLS works by collecting stream data into video segments—called chunks—that are transmitted sequentially. In other words, it requires time to collect enough data to create a chunk. For example, if the chunk size is set to 10 seconds, transmission cannot begin until 10 seconds have elapsed. As a result, the total latency will exceed 10 seconds.
In contrast, RTMP continuously transmits data from an encoder in real time without interruption. This means, it requires that the data should be delivered to the player ① just on time, ② in the correct sequence, and ③ without any corruption. If any one of these three conditions is compromised for any reason, it will result in video playback issues.
In summary, RTMP and HLS transmissions have the following characteristic.
- RTMP
- Relatively low transmission latency.
- Sensitive to the quality of the transmission network.
- HLS
- Requires time to create chunk
- Relatively insensitive to the quality of the transmission network.
RTMP vs HLS: Which protocol is suitable?
As seen above, RTMP and HLS each have their own characteristics, as well as distinct strengths and weaknesses. Then, how can the reader determine which protocol is the right choice for the YouTube live streaming?
For Instant Viewer Interaction : RTMP
For content that requires real-time interaction with viewers, such as game streaming, the low latency of RTMP is a better option.
When using HLS, even with YouTube’s minimum recommended chunk size of two seconds, the response time to viewers is at least four seconds. This latency is further extended by YouTube’s internal transcoding and transmission times. Excessive latency negatively impacts the real-time interaction experience.
For Latency-Sensitive Content : RTMP
If the content is sensitive to spoilers, such as live sports or major announcements, the low latency of RTMP is a significant advantage. This helps avoid situations where a viewer might hear a cheer from their neighbor watching the broadcast feed moments before they see the goal on their own stream.
For Long-Duration Broadcasts : HLS
Three hours is enough time for network conditions to change. (In fact, it can change from minute to minute.) An RTMP stream is sensitive to network conditions, so if an initially stable network environment degrades over time, the stream’s quality can be affected. Therefore, to maintain a consistently stable stream, it is more advantageous to use HLS, as it is less susceptible to network fluctuations.
For Unstable Network Conditions (e.g., Wi-Fi) : HLS
With RTMP, even a single error during transmission can cause playback issues. HLS, in contrast, allows for continuous playback even if momentary transmission errors occur, as long as the data is delivered within the required time. Therefore, it is better to use HLS when streaming over Wi-Fi or on any wired connection with poor network quality
The Writer’s Recommendation: HLS
The internet is less stable than people might think. While domestic traffic tends to be less affected, international traffic faces limitations due to exchange capacity. Moreover, the long undersea fiber-optic cables that carry global data are vulnerable to environmental factors, which can further impact stability.
Indeed, the reader has likely experienced how even local weather can affect the quality of the internet connection.
The video above shows the same live stream source being sent to YouTube from the same server. The RTMP stream on the left experiences continuous stuttering, while the HLS stream on the right can be seen playing back stably.
For these reasons, the writer recommends using HLS as the default for YouTube live streaming
Summary FAQ
- Is it possible to stream using HLS from OBS?
- Yes, it’s possible. In OBS’s broadcast settings, if you select YouTube as the service, it offers an option to use the HLS protocol in addition to the standard RTMP method that uses a stream key.
- If the network is unstable, shouldn’t both RTMP and HLS be affected?
- RTMP works ike a real-time call, data must be delivered continuously with minimal delay. If the data is interrupted even briefly or arrives out of order, it immediately affects the broadcast quality.
- HLS uploads fixed segments of video (e.g., 10-second “chunk” files) to the server. Even if a temporary transmission error occurs, as long as the file is successfully uploaded within the allowed time, it works fine. This extra time allows for multiple retry attempts. That retry capability is exactly why HLS tends to be more stable in unstable network environments.
- Which protocol is more stable between HLS and RTMP?
- HLS is significantly more stable. HLS transmits segmented files and allows for retries, making it more resilient to temporary network instability. In contrast, RTMP relies on a continuous connection, and even a brief interruption can directly affect the stream quality.
- If I’m using a 10Gbps fiber-optic internet plan, shouldn’t the connection be stable?
- Bandwidth (speed) and stability are different concepts. A wide bandwidth of 10Gbps means the ability to transmit a large amount of data at once, but it does not guarantee the stability of that data—whether it gets interrupted or lost during transmission. Especially for streaming services like YouTube that route through overseas servers, the connection can become unstable at any point along the international network path, regardless of the quality of your local internet connection.
- Is there any way to reduce HLS latency?
- Yes, there is. A standard technology called LL-HLS (Low-Latency HLS) has been developed to significantly reduce the structural latency of traditional HLS. By using LL-HLS, it’s possible to maintain HLS’s high stability while dramatically lowering the delay.
- Does transmission delay only affect playback?
- If transmission delays accumulate, the unsent data builds up in the server’s memory, which can eventually cause the server to down.